The Impact of Smoking on Heart Health
Smoking is a habit that millions of people around the world struggle with. While the detrimental effects of smoking on lung health are widely known, its impact on heart health is equally concerning. In fact, smoking is a leading cause of preventable heart disease and contributes to a range of cardiovascular problems. In this article, we will explore the specific ways in which smoking affects the heart and discuss the importance of breaking free from this harmful habit.
- Increased Risk of Heart Disease: Smoking damages the lining of the arteries, leading to the buildup of fatty deposits called plaque. This process, known as atherosclerosis, narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow to the heart. Consequently, smokers are at a significantly higher risk of developing coronary artery disease, angina (chest pain), heart attacks, and strokes.
- Higher Blood Pressure: The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause an immediate increase in blood pressure. Over time, this sustained elevation can damage the arteries and weaken the heart muscle. Smokers are more likely to develop hypertension (high blood pressure), which further contributes to the risk of heart disease.
- Reduced Oxygen Supply: Smoking decreases the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood by binding to hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen. This means that the heart and other vital organs receive less oxygen, putting additional strain on the cardiovascular system.
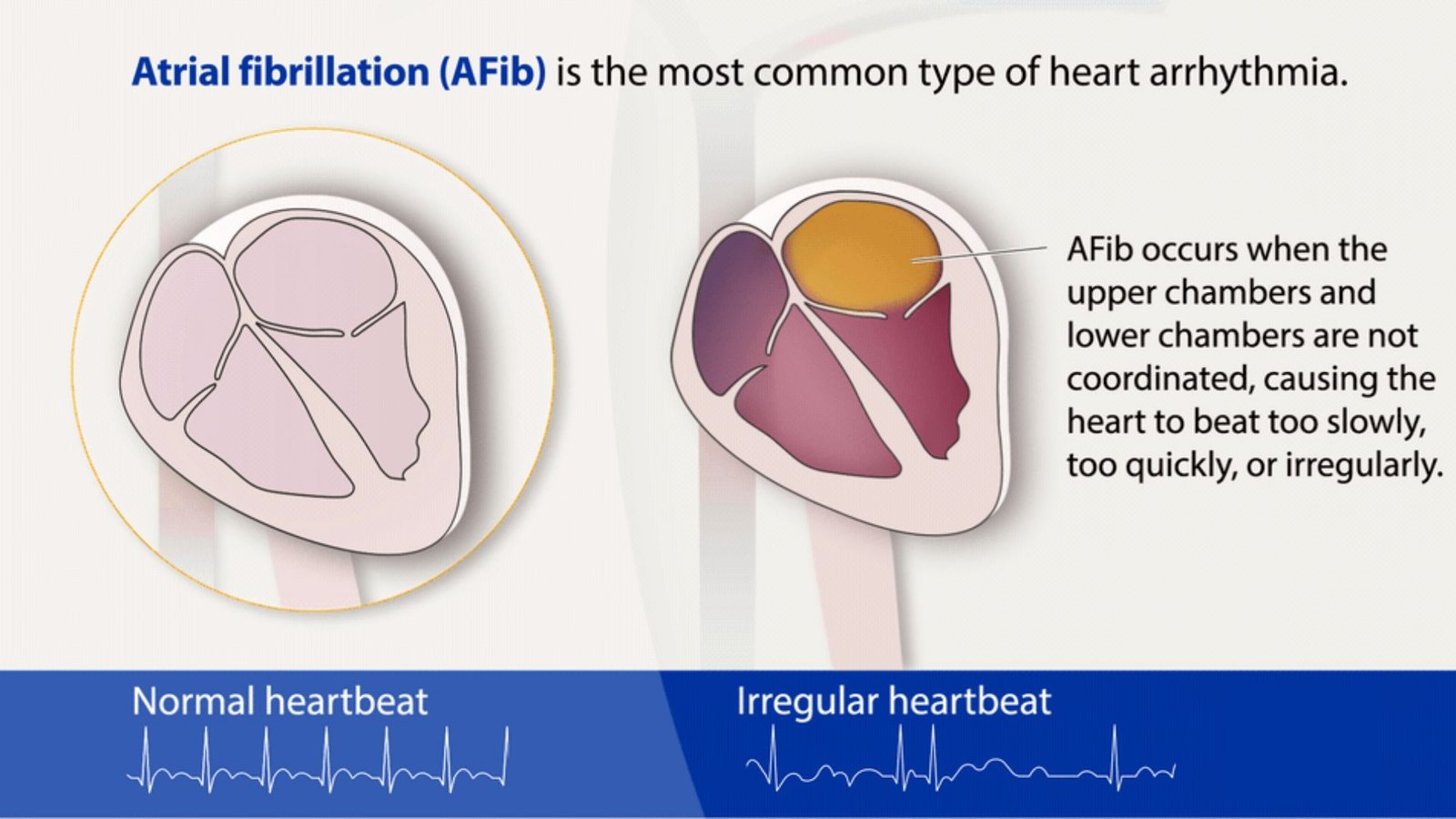
- Abnormal Heart Rhythms: Smoking disrupts the normal electrical activity of the heart, leading to irregular heart rhythms or arrhythmias. These irregularities can range from palpitations to potentially life-threatening conditions such as atrial fibrillation.
- Increased Blood Clotting: Smoking promotes the formation of blood clots, which can block blood vessels and cause heart attacks or strokes. The clotting factors in the blood are altered by the toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke, making smokers more prone to dangerous clot formation.
Breaking Free from the Habit:
- Seek Support: Quitting smoking can be challenging, but it’s not impossible. Reach out to your healthcare provider, join support groups, or enlist the support of friends and family to help you on your journey to quit smoking.
- Set a Quit Date: Choose a specific date to quit smoking and mentally prepare yourself for the change. Discard all smoking paraphernalia, such as cigarettes and lighters, and commit to a smoke-free lifestyle.
- Nicotine Replacement Therapy: Consider using nicotine replacement products, such as nicotine gum, patches, or lozenges, to help manage withdrawal symptoms and gradually reduce nicotine dependence.
- Behavioral Therapy: Explore behavioral therapy techniques, including counseling and cognitive-behavioral therapy, to address the psychological and emotional aspects of smoking addiction. These strategies can help identify triggers and develop coping mechanisms.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopt a healthy lifestyle to support your journey toward quitting smoking. Engage in regular physical activity, eat a balanced diet, and manage stress through activities like meditation or yoga.
- Stay Persistent: Quitting smoking may involve setbacks and challenges. Stay persistent and resilient, remembering the long-term benefits of a smoke-free life. Celebrate small victories and seek professional help if needed.
Remember, quitting smoking is one of the most impactful steps you can take to improve your heart health and overall well-being. Breaking free from this harmful habit not only reduces your risk of heart disease but also enhances your quality of life. Make the decision today to prioritize your heart and embrace a smoke-free future. Your heart will thank you.