With CABG, a surgeon takes a section of a healthy blood vessel from the patient’s leg, chest, or arm and connects it (grafts it) to their coronary artery slightly past the site of the blockage. This creates a new path for blood to flow around (bypass) the blockage in the artery so it can get to the heart.
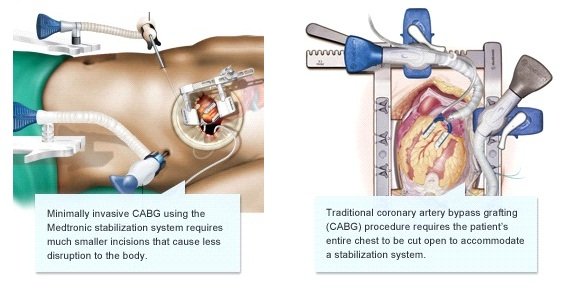
In traditional off-pump CABG (OPCAB), a large incision is made in the patient’s chest. This gives the surgeon access to the heart and is needed to accommodate a stabilization system that keeps the beating heart steady so the surgeon can sew on the replacement blood vessel.
However, a minimally invasive stabilization system can be inserted via small incisions on the sides of the chest. The system includes a heart positioner that holds the heart in a position that gives the surgeon access to the blocked arteries and a tissue stabilizer that holds a small area of the heart still while the surgeon works on it.
Our innovative placement of the stabilization system allows the surgeon to make a much smaller incision near the heart. When this technique and product are combined with our other minimally invasive techniques and products for CABG, the results can be significant.
Studies show this minimally invasive procedure results in shorter hospital stays and a faster return to daily living.
Benefits of Key-Hole Bypass:
- Very cosmetic
- Painless
- Early discharge in 3 days from hospital
- Early return to work




