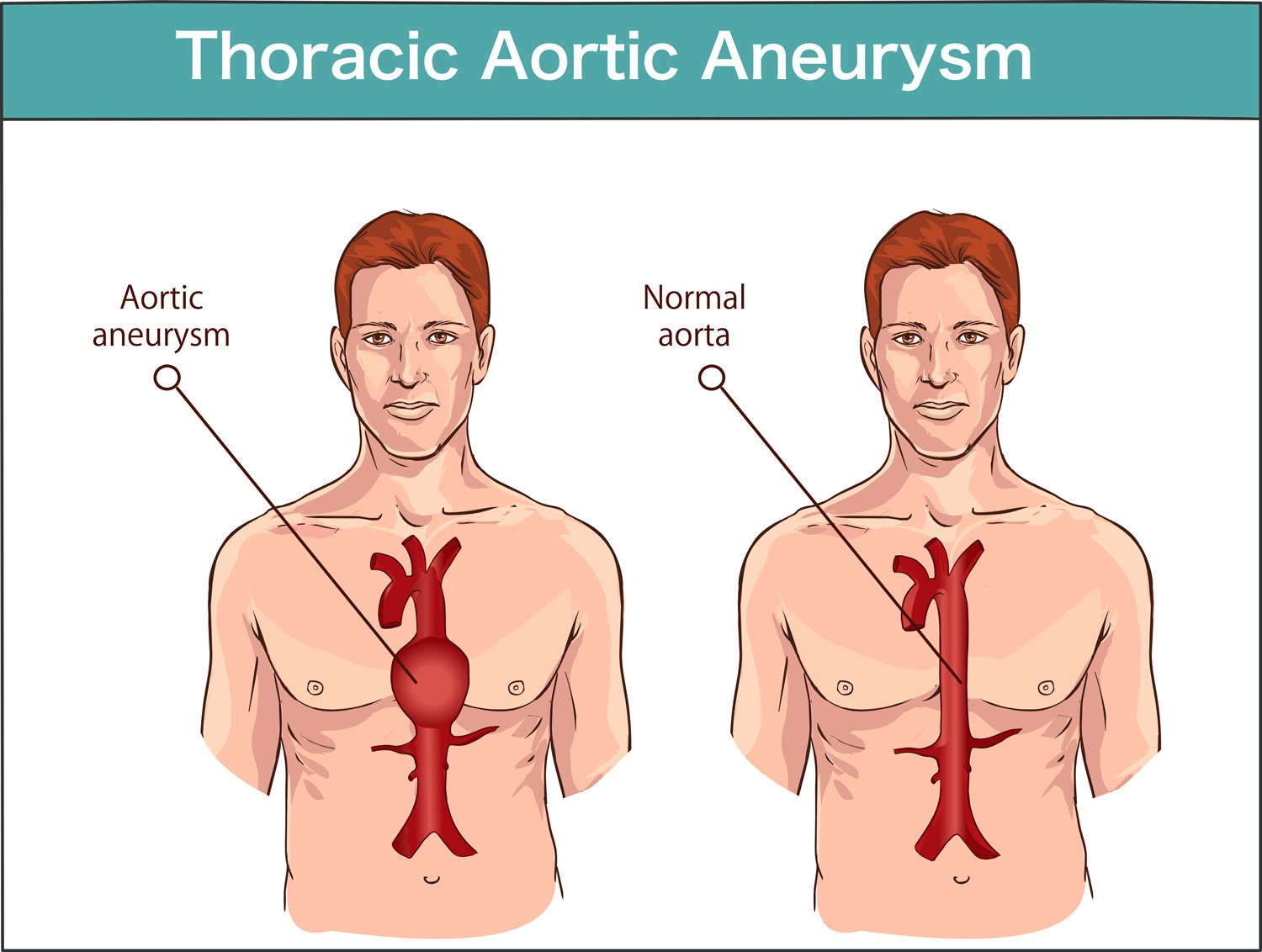
Did You Know What a Thoracic Aortic Dissection Is?
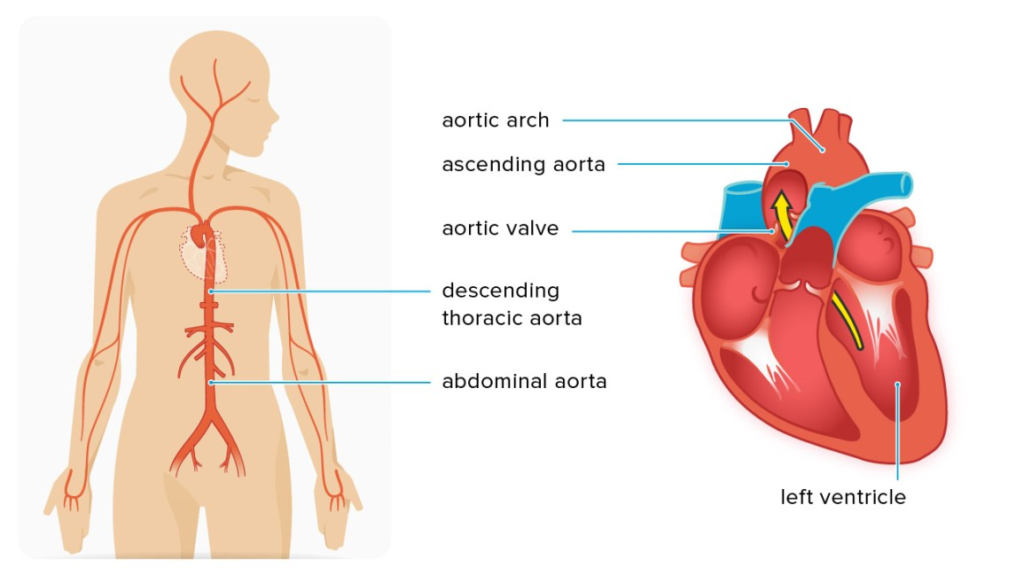
What is the Aorta?
The aorta is undoubtedly the largest and most important blood vessel in the human body. It originates in the heart and passes through two chambers, the thorax, and the abdomen until it undergoes a division at the level of the navel.
During its journey, it emits arterial branches rich in oxygenated blood, which goes to the arms, the brain, and all the vital organs such as the kidneys, intestines, and lower limbs, among others.
The dissection of the thoracic aorta is a break of its inner wall, called the inner layer. When this rupture occurs, the aorta internally divides in two, and blood can be distributed unevenly between the organs.
The incidence of aortic dissection in the world is about 6 new cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year.
Causes of thoracic aortic dissection
Thoracic aortic dissection usually occurs due to structural problems in the wall of this vessel. Didactically we can separate them into two groups:
- The first is the one in which the patient, severely hypertensive and a long-term smoker, on average 60 years of age, will present chronic damage to the inner layer of the aorta, until one day it may rupture. There are times when the patient already has a dilated aorta that precedes the dissection.
- The second is a group of younger patients, 30 to 40 years old, who suffer from genetic diseases such as Marfan, Ehlers-Danlos, and Turner Syndrome among others, or have a structural change in the heart called the bicuspid aortic valve. Some of these genetic syndromes involve collagen problems, and patients have structural changes in the middle layer of the aorta, which may one day be dissected.
Other less frequent situations, but that can also be triggers for aortic dissection, are pregnancy, trauma, and the use of illicit drugs, especially cocaine.
Symptoms of thoracic aortic dissection
The most common symptom in the acute phase is severe chest pain. Some patients report having the distinctive sensation of something breaking or tearing within them.
The main differential diagnosis is acute myocardial infarction. Other mild chest pains, such as muscle pain or dyspeptic seizures (gastritis), can also be considered.
Pain in the neck, back, or abdomen may also be reported.
Treatment for thoracic aortic dissection
Initial treatment consists of stabilizing the patient’s blood pressure, sometimes with intravenous therapy and rapid reconstructive surgery if a risk of cardiac tamponade or organ system ischemia is identified.
When the initial portion of the ascending aorta is affected, close to the outlet of the heart, it is usually necessary to perform open surgery, opening the sternum, and change the diseased portion of the aorta for a Dacron prosthesis.
Most ischemic organ correction techniques and interventions in other portions of the Aorta now receive full endovascular therapy, with less patient morbidity and faster recovery.
For more information on this disease and treatment options, consult Dr. Ritwick Raj Bhuyan.
Director: Department of Cardiovascular Surgery
Fortis Escorts Heart Institute & Research Centre, Okhla
New Delhi, India
——–
For Appointments
P| +91 9870217444
P| +91 9911065980
P| +91 9999802642
W| +91 9911065980 (WhatsApp)
Email: cardiacsurgeryonline@gmail.com